Although many homeowners would like a more aesthetically pleasing and healthy landscape, the results are not achieved with sporadic watering. A residential irrigation design plan uses water better within the landscape. Modern irrigation design involves evenly distributing the water, reducing the wastage, maintaining the yard’s sustainability, and providing the plants adequate moisture without runoff and overwatering problems during operation of systems.
Custom plans that include a layout and pressure analysis, as well as zone separation, can save homeowners plenty of money in the long run, as well as reduce stress to the plants and provide substantial efficiency in the yard. Residential irrigation design plans can allow a household to maintain a beautiful lawn for years, even decades. This article will discuss the rationale behind residential irrigation design plans and how a homeowner can best utilize them.
Overview, Basics, and Importance of Irrigation Planning
Residential irrigation design plans are blueprints for the layout of the irrigation system in a residential landscape, denoting where pipes, sprinkler heads and watering zones will be located. A well-designed plan for an irrigation system will eliminate common problems with insufficiently-designed systems like dry areas, pooling water and over/under-pressure on plants.
Professional design of such systems requires a site assessment. This includes soil conditions, slope, sunlight, and existing plants. These conditions will determine pipe size selection, water pressure selection, and nozzle specification selection for optimization of water distribution while waste minimizes.
| Element | Purpose | Benefit |
| Zone Layout | Separates areas with different watering needs | Prevents under or overwatering |
| Pipe Sizing | Ensures proper flow and pressure | Improves system efficiency |
| Sprinkler Head Placement | Defines radius and coverage consistency | Reduces overlap and dry spots |
| Controller Programming | Sets schedules and timing | Saves water and supports plant health |
Irrigation systems that are well-planned help homeowners find issues and change watering times, and make the project last by bettering how water resources are managed and how vegetation is doing.
Detailed Breakdown of How Irrigation Design Works
The design of a residential irrigation system incorporates many factors that affect how water is delivered and received into and through the ground.
Assessing the Landscape and Water Requirements
Designers will look closely at the site’s shape, plants, and soil during site analysis. Sandy soils drain quickly and need watering with more frequency. Clay soils retain water with more ease and require careful drainage. Several watering cycles may help stop excessive water entry into the soil of tilted properties.
Designers then determine the peak water demand for each zone to comply with the maximum amount of water that can be supplied without creating a strain on the system when a sprinkler head or drip line is running.
Creating a Functional and Efficient System Layout
The designer uses the information to create a scaled drawing of the entire system with all valves, pipes, sprinklers, and controllers shown. Each sprinkler head is commonly set in a head-to-head design so the spray from each gets to the bottom of the neighboring head.
Pressure management requires the installation of pressure-balancing valves in areas with different elevations. This keeps the system functioning properly and reduces misting and the wastage of water that can be caused by it. It also gives each controller the ability to provide tailored watering.
Comparison of Irrigation Methods and Case Examples
Prior to residential irrigation design, homeowners weigh the pros and cons of each of these systems based on factors such as the location of their yard, climate, and plant selection.
Irrigation Method Efficiency Comparison
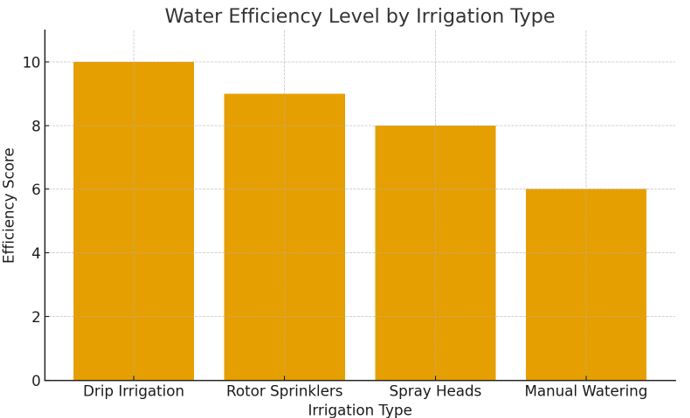
- Water use efficiency of Drip Irrigation, Rotor Sprinklers, Spray Heads and Manual Watering is summarized in the following table.
- Drip Irrigation gets 10 points because this process waters the roots of plants directly, which is the most efficient method.
- At a score of 9, Rotor Sprinklers outperform other commercial sprinklers due to controlled rotation.
- Spray Heads score 8, offering good coverage, but their downside is that they waste more water through evaporation or overspray.
- Manual Watering scores lowest (6) since it results in uneven watering and greater water waste.
- Overall, the graph shows how automatic, precision-based systems are better at conserving water and creating healthy landscapes than manual systems.
Drip irrigation systems deliver water close to the roots, and are the most efficient. Rotor sprinklers are best for covering large areas of lawn. Spray heads are efficient in watering small areas but inefficient in windy conditions. Manual watering is least efficient as overlapping depends on staffing and time.
Case Study Example
This suburban home with a yard containing flower beds and a large expanse of grass was fitted with a hybrid installation of drip irrigation for flower beds and rotor sprinklers for the grass using residential irrigation design plans. The homeowner saved almost 40 percent on their water bill and improved the health of the plants.
Practical Tips for Choosing or Creating the Right Irrigation Plan
Homeowners can create and implement irrigation plans that are based on a number of practical steps in order to ensure that the systems are appropriate for the property.
Evaluate the Landscape Thoroughly
Knowing the soil type, the sun conditions and the slope helps determine the optimal means to irrigate and reduce waste.
Choose the Right Irrigation Method
Drip systems are useful for beds of plants, while rotor sprinklers are useful for large turf areas. The two can be used together.
Consider Future Plant Growth
However, trees and shrubs may grow, requiring changes in the configuration of the sprinkler heads.
These guidelines ensure that plans for residential irrigation systems promote the long-term performance of systems.
Recap
The planning of irrigation landscapes artist designs in particular can lead to healthy, sustainable landscapes. Residential irrigation designs must create an efficient, lasting water supply, while conserving water. Proper site information arrangement, system design, and controller scheduling help maintain plant health and save water during irrigation.
If someone creates a well-planned irrigation system, it covers well and performs without dry areas, too much runoff, or a high water bill. This guide covered how to create an irrigation plan, types of irrigation systems, and how to choose the best system for your home according to needs.
In short, a well-designed irrigation system is one of the smartest investments a homeowner can make toward improving the health of their landscape along with saving water and watering effectively for years to come.

