A healthy residential landscape includes a planned irrigation system. Residential irrigation design plans help homeowners provide adequate watering for lawns, gardens and plants throughout property without over- or under-watering property. Poor irrigation design can cause dry spots, over-watering, and high utility bills.
Modern people conserve water for sustainability and minimize future maintenance by changing how they plan and implement irrigation. Irrigation is no longer a process of locating sprinklers, but is based on soil, plant, climate, and zoning with consideration of aesthetics and water use.
This article describes residential irrigation systems. It explains their design and planning. The article includes what they are. The article includes how to plan them. The article lists their advantages and disadvantages. The article shows how to choose one for your property. Homeowners aim to get practical information to install irrigation systems for effective work through many years.
What Are Residential Irrigation Design Plans and Why They Matter
The residential irrigation design plan is a custom drawn plan outlining the irrigation zones, equipment locations, water pressure, and watering schedules that accomplish the goal of watering the landscape of a residential home while minimizing excess water use.
Residential irrigation design plans are important for the efficient use of water since each plant has different requirements and one irrigation type is rarely applicable everywhere. A good design will break lawns, shrubs, and garden beds into groups that have similar needs.
Life expectancy of the system is affected as well, since good design will reduce the stress on pipes, valves and sprinkler heads, lowering maintenance costs and preventing frequent repair.
Design plans are also helpful within sustainability efforts, as proper irrigation can prevent water wastage and runoff, and for regions with irrigation limitations, an expert plan can aid in maintaining a beautiful landscape.
| Aspect | Poorly planned irrigation | Designed irrigation plan |
| Water use | Excessive | Efficient |
| Plant health | Inconsistent | Balanced |
| Maintenance | Frequent repairs | Reduced issues |
| Long-term cost | High | Controlled |
How Residential Irrigation Design Plans Are Developed
Irrigation systems have to be planned, analyzed, and engineered out. Each property includes unique needs and problems.
Site evaluation and zoning
Designers do a landscape analysis, considering the types of soils, slope, amount of sunlight, and plants in the area because these affect both the flow and absorption of water.
Zoning is important. Group similar water-need areas. Lawns, ornamental plants, and trees are irrigated separately for prevention of under- or over-watering.
Equipment selection and layout
Irrigation components like sprinkler heads, drip lines, valves, and controllers are chosen after zones are created. Their positioning will be based on even coverage.
Residential irrigation design plans consider water pressure and water flow rates, and require calculations to avoid uneven watering.
Scheduling and efficiency planning
The design plans may specify the watering schedule, depending on the climate and plants; smart controllers can also be used to adjust the schedule.
Key design considerations include:
- Soil and slope analysis
- Irrigation zoning by plant type
- Proper equipment selection
- Water pressure and flow balance
Comparing Different Irrigation Design Approaches
Irrigation systems differ such that examples show benefits and drawbacks.
Most basic systems use uniformly spaced sprinklers that may waste water after a period of time; more advanced systems use zoned or target-specific delivery.
Flexibility during the design process of residential irrigation systems allows for plant growth and seasonal variations, leading to landscape sustainability.
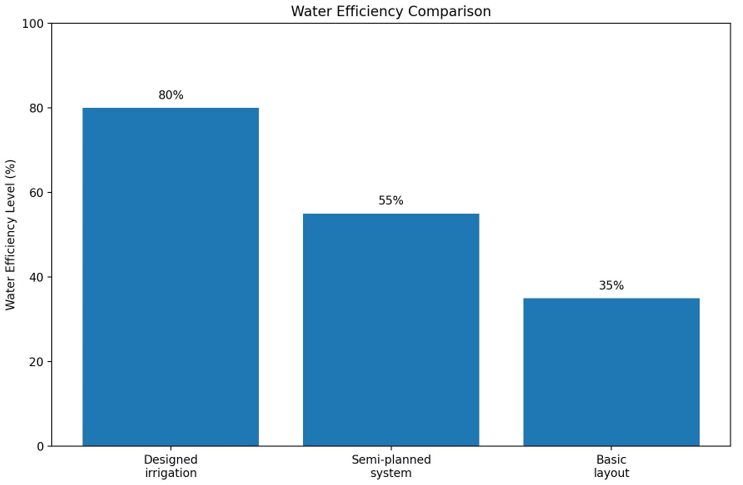
- Designed irrigation systems have great efficiency. They water with precision. They waste very little.
- Semi-planned systems may have improved efficiency but risk unsupervised low coverage or overwatering.
- Basic layouts tend to use more water due to less zoned control and more even sprinkler arrangements.
- High efficiency directly correlates to healthier plants, since zones match actual watering needs.
- Professional plans balance the need to reduce runoff and to avoid dry spots and streaks.
How to Choose the Right Residential Irrigation Design Plan
A successful irrigation plan is driven by landscape objectives including plant choice, property size, and the level of effort and resources devoted to maintenance.
Professional designers consider future growth and irrigation needs of plants, and design accordingly, so a change can occur in the future.
Budgeting is also a major consideration. While a designed system may be more costly initially, it tends to save money in the long run. Water costs decline and repairs occur less frequently over time.
It helps to consider the region’s climate, when designing residential irrigation, to ensure the plans work better and function effectively for longer.
Helpful selection tips include:
- Assess plant variety and layout
- Consider long-term water savings
- Choose adaptable, scalable designs
- Prioritize efficiency over short-term cost
Investing in Smart Irrigation Planning
Irrigation is not a solution that creates a healthy landscape by Land Scape artist Design. Residential irrigation design plans specify irrigation systems that work for years to come. They take water usage from a shot in the dark to a process.
This results in healthier plants, lower water bills, and less maintenance for you. A well conceived irrigation system can serve both aesthetic and conservation purposes too.
As people use water more critically, irrigation planned with careful design invests cost effectively in property for sustainability. Investing into a professional residential irrigation design plan helps ensure a durable, efficient, and stylish landscape around your home.

